网络编程
重点
网络分层
为了减少网络设计的复杂性,绝大多数网络采用分层设计方法。所谓分层设计方法,就是按照信息的流动过程将网络的整体功能分解为一个个的功能层,不同机器上的同等功能层之间采用相同的协议,同一机器上的相邻功能层之间通过接口进行信息传递。
- 网络模型(了解)
- 网络模型一般是指OSI七层参考模型和TCP/IP四层参考模型。这两个模型在网络中应用最为广泛。
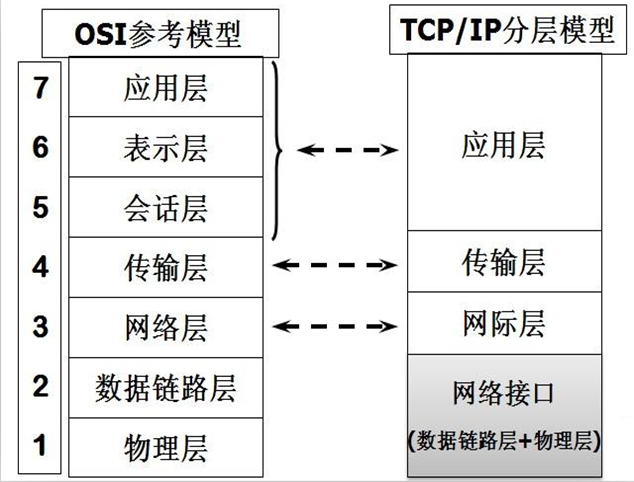
开放系统互连参考模型 (Open System Interconnect 简称OSI)是国际标准化组织(ISO)和国际电报电话咨询委员会(CCITT)联合制定的开放系统互连参考模型,为开放式互连信息系统提供了一种功能结构的框架。它从低到高分别是:物理层、数据链路层、网络层、传输层、会话层、表示层和应用层。
数据通讯过程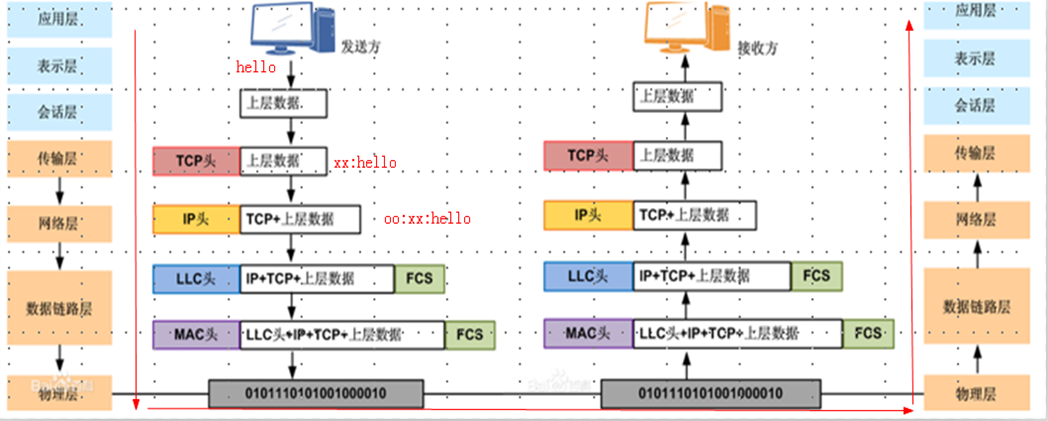
TCP/IP
TCP/IP是一组用于实现网络互连的通信协议。Internet网络体系结构以TCP/IP为核心。
基于TCP/IP的参考模型将协议分成四个层次,它们分别是:网络访问层、网际互联层、传输层(主机到主机)、和应用层。
- 应用层
应用层对应于OSI参考模型的高层,为用户提供所需要的各种服务,例如:FTP、Telnet、DNS、SMTP等. - 传输层
传输层对应于OSI参考模型的传输层,为应用层实体提供端到端的通信功能,保证了数据包的顺序传送及数据的完整性。该层定义了两个主要的协议:传输控制协议(TCP)和用户数据报协议(UDP).TCP协议提供的是一种可靠的、通过“三次握手”来连接的数据传输服务;而UDP协议提供的则是不保证可靠的(并不是不可靠)、无连接的数据传输服务. - 网际互联层
网际互联层对应于OSI参考模型的网络层,主要解决主机到主机的通信问题。它所包含的协议设计数据包在整个网络上的逻辑传输。注重重新赋予主机一个IP地址来完成对主机的寻址,它还负责数据包在多种网络中的路由。该层有三个主要协议:网际协议(IP)、互联网组管理协议(IGMP)和互联网控制报文协议(ICMP)。
IP协议是网际互联层最重要的协议,它提供的是一个可靠、无连接的数据报传递服务。 - 网络接入层(即主机-网络层)
网络接入层与OSI参考模型中的物理层和数据链路层相对应。它负责监视数据在主机和网络之间的交换。事实上,TCP/IP本身并未定义该层的协议,而由参与互连的各网络使用自己的物理层和数据链路层协议,然后与TCP/IP的网络接入层进行连接。地址解析协议(ARP)工作在此层,即OSI参考模型的数据链路层。
网络编程
什么是套接字
源IP地址和目的IP地址以及源端口号和目的端口号的组合称为套接字。其用于标识客户端请求的服务器和服务.
什么是网络编程
: 通过使用套接字来达到进程间通信目的的编程就是网络编程.
进程之间的通信:
- 在同一台电脑上,A进程和B进程相互通信.
- 在网络中(外网/内网),A电脑中的aa程序和B电脑中的bb程序相互通信(有网络连接).
为什么需要网络编程
:
- 如果没有网络,只能玩单机游戏.(斗地主,三国杀,CS等)
- 有了网络,QQ游戏等.
网络编程三要素
:
- IP地址.
网络之间互连的协议(IP)是Internet Protocol的外语缩写,中文缩写为“网协”.在Java中使用InetAddress类表示.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17package com.zhiyou100.net;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class TestIp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//根据主机名确定主机的IP地址
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getByName("DESKTOP-4DTSU5N");
System.out.println(ip.toString());
//获取主机名
System.out.println(ip.getHostName());
//获取IP地址
System.out.println(ip.getHostAddress());
//获取本机IP
System.out.println(InetAddress.getLocalHost());
//是否可以连接,与ping有点像
System.out.println(InetAddress.getLocalHost().isReachable(1000));
}
}IP地址编址方案将IP地址空间划分为A、B、C、D、E五类,其中A、B、C是基本类,D、E类作为多播和保留使用。
* A类 10.0.0.0--10.255.255.255 * B类 172.16.0.0--172.31.255.255 * C类 192.168.0.0--192.168.255.255表示本机
- 方式1:本机IP - 方式2:127.0.0.1 - 方式3:localhost
端口
- “端口”是英文port的意译,可以认为是设备与外界通讯交流的出口。端口可分为虚拟端口和物理端口,其中虚拟端口指计算机内部或交换机路由器内的端口,不可见。例如计算机中的80端口、21端口、23端口等。物理端口又称为接口,是可见端口,计算机背板的RJ45网口,交换机路由器集线器等RJ45端口。电话使用RJ11插口也属于物理端口的范畴。
- 协议端口
如果把IP地址比作一间房子 ,端口就是出入这间房子的门。真正的房子只有几个门,但是一个IP地址的端口可以有65536(即:2^16)个之多!端口是通过端口号来标记的,端口号只有整数,范围是从0 到65535(2^16-1)。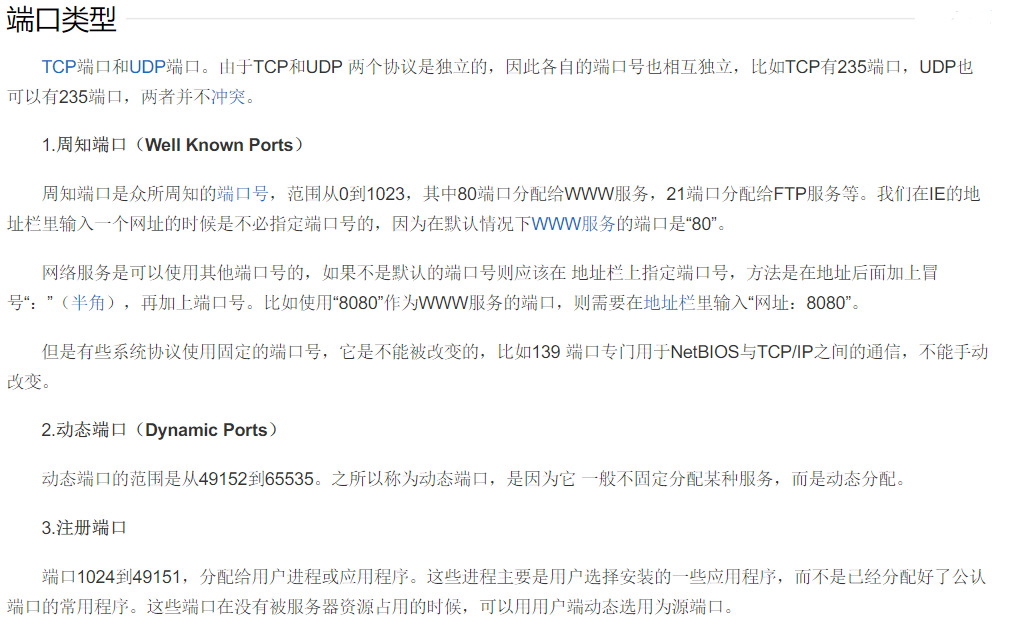
协议:规则,数据传递/交互规则.
协议(protocol),网络协议的简称,网络协议是通信计算机双方必须共同遵从的一组约定。如怎么样建立连接、怎么样互相识别等。只有遵守这个约定,计算机之间才能相互通信交流。它的三要素是:语法、语义、时序。
网络协议,也可简称协议,通常由三要素组成:
(1)语法:即数据与控制信息的结构或格式;
(2)语义:即需要发出何种控制信息,完成何种动作以及做出何种响应;
(3)时序(同步),即事件实现顺序的详细说明。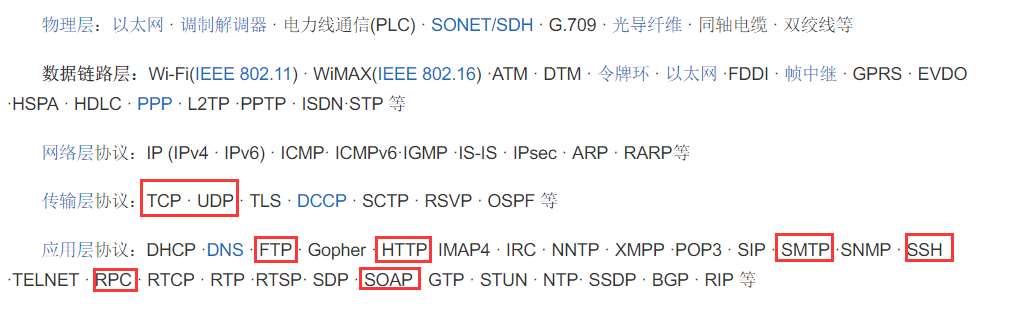
URI与URL
- URI
- 统一资源标识符(Uniform Resource Identifier,或URI)是一个用于标识某一互联网资源名称的字符串。
包含:主机名,标识符,相对URI.
如:https://www.baidu.com:80/index.php
- URL
- 统一资源定位符是对可以从互联网上得到的资源的位置和访问方法的一种简洁的表示,是互联网上标准资源的地址。互联网上的每个文件都有一个唯一的URL,它包含的信息指出文件的位置以及浏览器应该怎么处理它。
- 区别
- 在Java中
- URI表示一个统一资源的标识符,不能用于定位任何资源,唯一的作用就是解析.
- URL则包含一个可以打开到达该资源的输入流,可以简单理解URL是URI的特例.
简单理解: URI和URL都表示一个资源路径.
创建URL对象:
URL(String protocol, String host, int port, String file)
- 案例1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建URL对象
URL url = new URL("http", "www.baidu.com", 80, "/index.php");
//打开URL的连接对象
URLConnection con = url.openConnection();
//获取连接中的流数据
InputStream is = con.getInputStream();
//通过扫描器扫描输入流
Scanner sc = new Scanner(is);
String line = null;
//一次读取一行,打印到控制台
while(sc.hasNextLine()) {
line = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
}
sc.close();
is.close();
}
- 案例2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*//创建URL对象
URL url = new URL("http", "www.baidu.com", 80, "/img/bd_logo1.png");
//https://infinitypro-img.infinitynewtab.com/findaphoto/bigLink/10298.jpg
//打开URL的连接对象
URLConnection con = url.openConnection();
//获取连接中的流数据
InputStream is = con.getInputStream();
//通过Files工具类进行文件拷贝
Files.copy(is, Paths.get("login.png"));
is.close();*/
for(int i = 1188;i<3000;i++) {
downloadImgs(i);
}
}
public static void downloadImgs(int num) throws Exception{
//创建URL对象
URL url = new URL("http", "infinitypro-img.infinitynewtab.com", 80, "/findaphoto/bigLink/"+num+".jpg");
//https://infinitypro-img.infinitynewtab.com/findaphoto/bigLink/10298.jpg
//打开URL的连接对象
HttpURLConnection con = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
if(con.getResponseCode() == 200) {
//获取连接中的流数据
InputStream is = con.getInputStream();
System.out.println(url);
//通过Files工具类进行文件拷贝
Files.copy(is, Paths.get("D:\\test\\"+num+".jpg"),StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
is.close();
}
}
传输层的协议
TCP和UDP的区别
:
- TCP :面向连接(经历三次握手)、传输可靠(保证数据正确性,保证数据顺序)、用于传输大量数据(流模式)、速度慢,建立连接需要开销较多(时间,系统资源)。

服务端和客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建服务端,指定端口号为6666
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(6666);
System.out.println("服务端已启动");
//接受连接该服务端的客户端对象
Socket client = server.accept();
System.out.println("有一个客户端连接"+client.getInetAddress());
//服务端给客户端发个消息,获取客户端的输出流对象
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream());
ps.println("美女,你好");
ps.close();
server.close();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, IOException {
//创建客户端,指明服务端的主机和端口
Socket client = new Socket("localhost",6666);
//获取客户端的输入流对象,得到数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(client.getInputStream());
while(sc.hasNextLine()) {
System.out.println(sc.nextLine());
}
sc.close();
client.close();
}
}
**服务端向客户端不断发送消息**
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建服务端,指定端口号为6666
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(6666);
System.out.println("服务端已启动");
//接受连接该服务端的客户端对象
Socket client = server.accept();
System.out.println("有一个客户端连接"+client.getInetAddress());
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream());
ps.println(str);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, IOException {
//创建客户端,指明服务端的主机和端口
Socket client = new Socket("localhost",6666);
while(true) {
//获取客户端的输入流对象,得到数据
Scanner sc = new Scanner(client.getInputStream());
while(sc.hasNextLine()) {
System.out.println(sc.nextLine());
}
sc.close();
}
}
}
**类QQ**-客户端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Socket client = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
System.out.println("客户端已启动");
// 1.启动线程用于写给服务器
new ClientRead(client).start();
// 2.启动线程用于读取服务器的数据
new ClientWrite(client).start();
}
}
class ClientRead extends Thread {
private Socket client;
public ClientRead(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
}
public void run() {
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(client.getInputStream()));
String line = "";
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (!"".equals(line) && line != null) {
System.out.println("服务器说:" + line);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 读键盘,写到服务器
*
* @author zhang
*/
class ClientWrite extends Thread {
private Socket client;
public ClientWrite(Socket client) {
this.client = client;
}
public void run() {
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(client.getOutputStream()));
String str = "";
while (true) {
str = input.readLine();
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
**类QQ**-服务端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8888);
System.out.println("服务器已经建立,,等待客户端连接。。");
Socket socket = server.accept();
System.out.println("已有客户端连接。。。");
// 读,或者写
// 启动线程,用于读客户端的数据
new ServerRead(socket).start();
// 启动线程,用于向客户端写数据
new ServerWrite(socket).start();
}
}
/**
* 读客户端的数据:socket中输入流,读,打印输出
*
* @author zhang
*
*/
class ServerRead extends Thread {
private Socket s;
public ServerRead(Socket s) {
this.s = s;
}
public void run() {
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String line = "";
while (true) {
line = br.readLine();
if (!"".equals(line) && line != null) {
System.out.println("客户端说:" + line);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
/**
* 向客户端写数据:socket中获取输出流,读键盘,写给客户端
*
* @author zhang
*
*/
class ServerWrite extends Thread {
private Socket socket;
public ServerWrite(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
public void run() {
// 1.获取流
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
String str = "";
// 2.循环向客户端写数据
while (true) {
str = input.readLine();
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
- UDP:面向无连接、传输不可靠(丢包[数据丢失])、用于传输少量数据(数据报包模式)、速度快。发送端和接收端
客户端和服务端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public class Send {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String data = "你好,美女";
//创建发送端对象
DatagramSocket sender = new DatagramSocket(6666);
//发送数据
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(data.getBytes(),
0, data.getBytes().length,
InetAddress.getLocalHost(),
10086);
sender.send(dp);
sender.close();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class Receive {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DatagramSocket receiver = new DatagramSocket(10086);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buffer,1024);
receiver.receive(dp);
String msg = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
System.out.println(msg);
}
}